
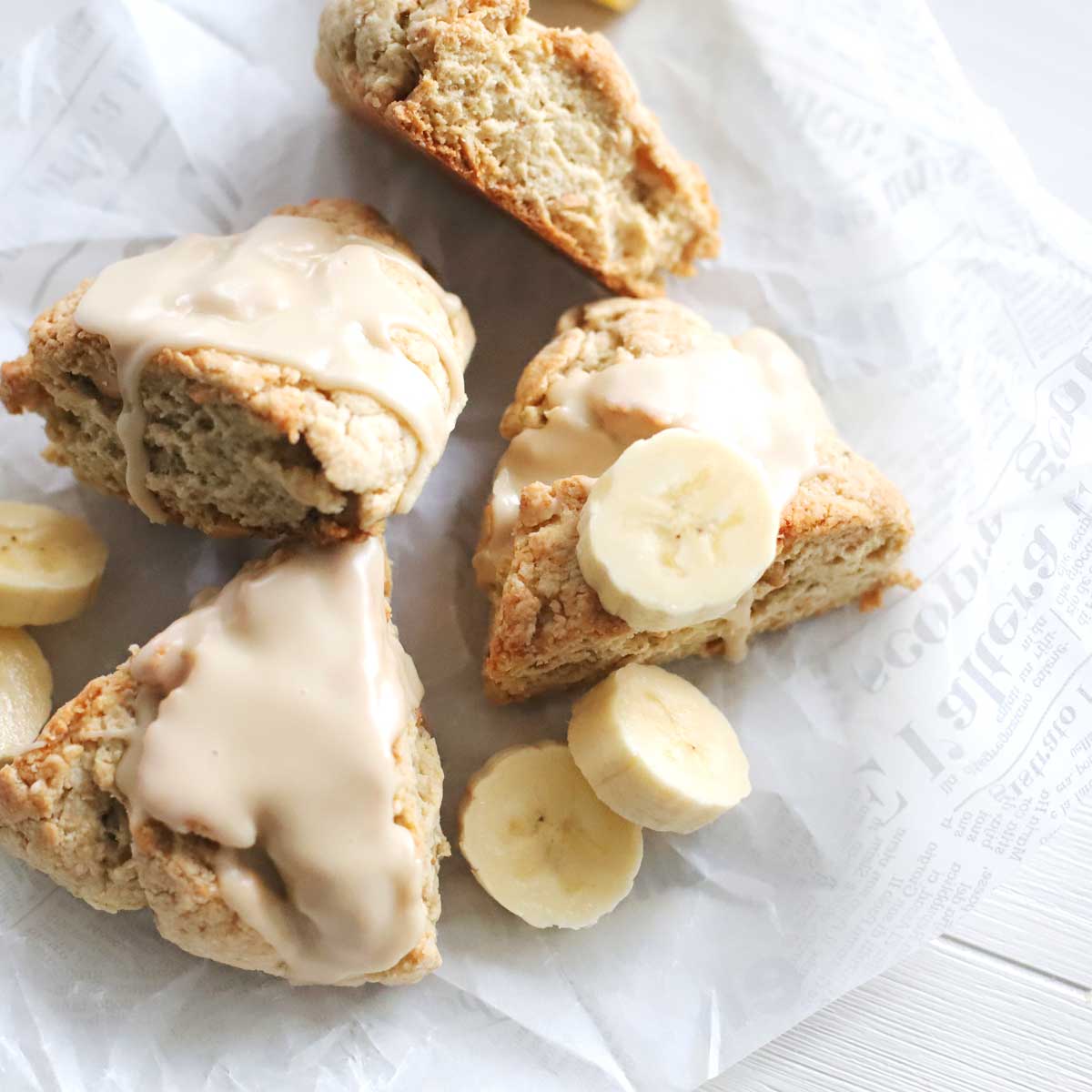
What are Bananas?
Bananas are among the world's most popular fruits, with more than 150 countries cultivating over 105 million tonnes every year. It is one of the most eaten fruits. According to some estimates, more than 100 billion bananas are consumed each year globally. It is estimated that bananas are originated in Southeast Asia and the South Pacific around 8000 to 5000 BC. From Southeast Asia, the fruit was brought west and then carried worldwide by explorers and missionaries. There are two variants of a banana: Unripe and Ripe banana. Both of them are nutritionally rich and consumed by people worldwide. Unripe bananas have a slightly bitter taste, firm texture and green color. In contrast, ripe bananas are sweet and have a yellow color.
How Many Calories is a Banana?
There are 89 calories in a 100g serving of ripe bananas according to the USDA database.
| Small (6”–6-⅞”) | 101 grams | 90 calories |
| Medium (7”–7-⅞”) | 118 grams | 105 calories |
| Large (8”–8-⅞”) | 136 grams | 121 calories |
| Sliced, 1 cup | 150 grams | 133 calores |
| Mashed, 1 cup | 225 grams | 200 calories |
Health Benefits of Banana
Most people enjoy eating bananas as well. It can be eaten alone, combined with a fruit salad, or made into a smoothie. They are also one of the most affordable fruits and are available year round and everywhere globally. Bananas are an excellent source of potassium. A single banana provides 23% of the potassium that we need daily. Recent studies demonstrated that potassium can help to decrease blood pressure and reduce the risk of stroke. Bananas are also an excellent source of vitamins A, B6, C, and D that aids in healing, increases your focus and mental acuity. Some studies show that bananas can help improve your mood, and that they even improve PMS symptoms in women.

How to Pick Bananas
When you want to buy bananas, pay attention to the bunches first. Fresh banana bunches still look green. If the color is brown, it indicates that the bananas have been harvested for a long time. For immediate consumption, it's best to choose bananas with some yellow with brown spots, which means that they are already ripe. If you want to use or eat bananas for later, you should pick bananas that are slightly green. The best bananas are bright in color, full and plump, and without any bruising. Darker, or moist (depressed) areas on the banana skin usually signal that the fruit’s inside is bruised. A dull, grey color indicates they have been either chilled or overheated during storage. If you cannot easily break the stem to peel the banana, it is not yet ripe (suppose the skin is difficult to separate from the fruit). In that case, it is most likely too starchy and bitter to eat (without cooking), so it could cause digestive distress and constipation if eaten raw.
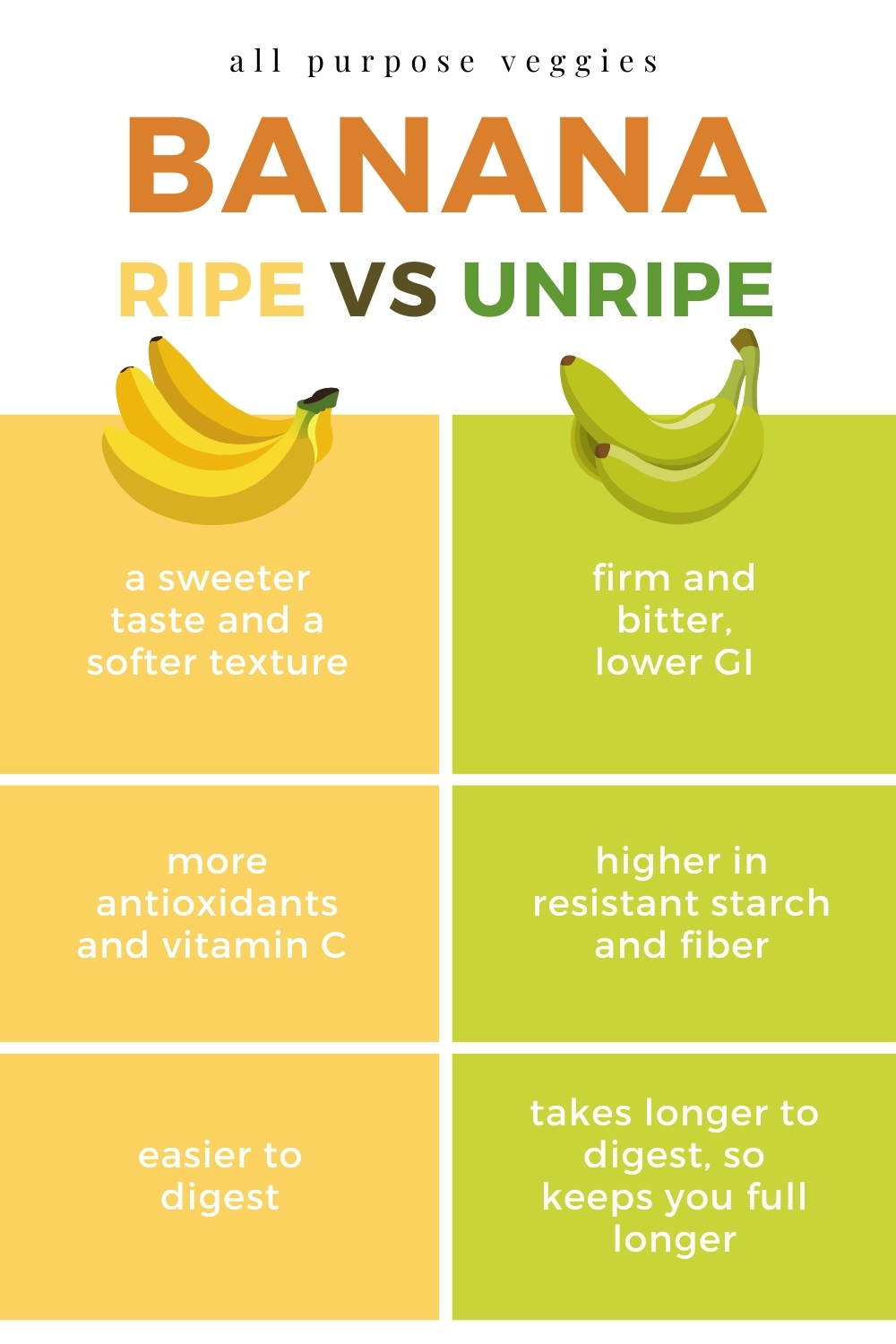
Banana Ripe vs Unripe
Green bananas are good sources of fiber (21.91 g/100g) and resistant starch (68.02 g/100g). Resistant starch contains calories that are lower than the calories of carbohydrates in general. If usually, 1 gram of carbohydrates contains four calories, resistant starch contains only two calories per gram. In addition, resistant starch has almost the same function as fiber. Thus, resistant starch in bananas can give the body a longer full effect. This can prevent you from feeling hungry. Several studies show that the resistant starch and fiber content of green bananas can help manage body weight and diabetes. The resistant starch in a green banana is the highest among the others. Still, the resistant starch will turn into fructose, glucose, and sucrose as it ripens.
Unlike the green bananas, the ripe bananas have a sweeter taste and a softer texture. A study shows that antioxidants and vitamin C increased during the ripening process. The antioxidant activity was higher in fully ripe bananas. Also, the ripening process raises the sugar content as well. Suppose unripe bananas contain resistant starch that can reduce body weight. In that case, ripe bananas may help prevent the side effect of green banana consumption, such as constipation. Some studies show that antioxidants in bananas have anti-inflammatory, antiallergic properties and reduce cardiovascular disease.
Can you freeze Mashed Banana?
Yes! Mashed bananas can be frozen for later use and can be used in baked goods just as you would use fresh mashed bananas.




























































Leave a Reply